Robert Morris University
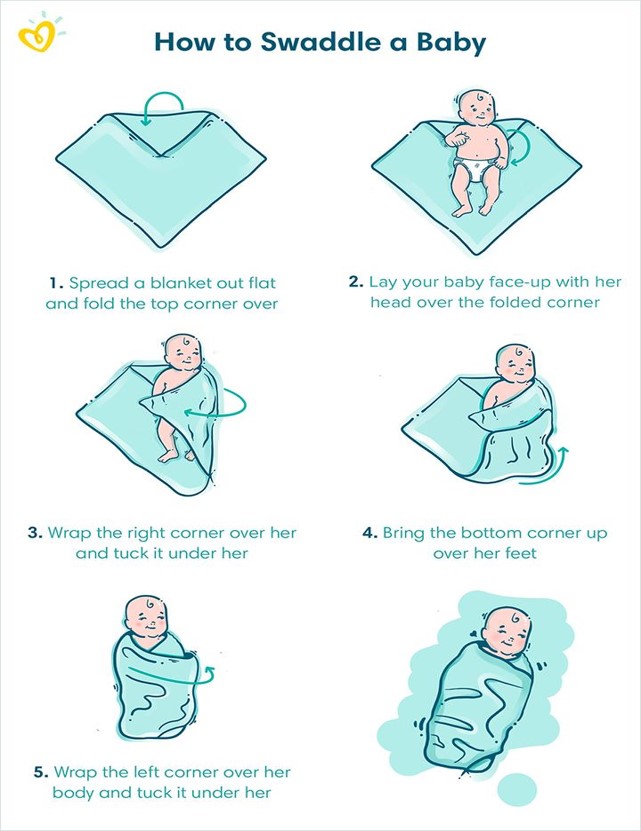
Premature Infants
●85% of preterm births happen between 32 and 37 weeks gestation
●Some reasons some women are at risk for their babies coming early are:
○High blood pressure
○Low iron (anemia)
○Short intervals between babies
○Infections
●These infants do not usually require special care for survival, but there may be some babies that do.
Full Term versus Preemie
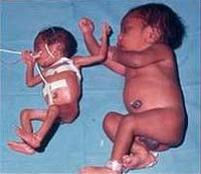
Full Term
●The baby has been in the womb for 37
weeks or more
Preemie
●The baby is born before 37 weeks gestation
●A baby may not be as developed if they are born before 37 weeks, so skin to skin contact is encouraged
●Baby may have more Lanugo (body hair) if they are premature – NORMAL
●Smaller in size
●Have less body fat
●Thinner skin
●May not nurse or suck as well when eating
●Often needs help to keep warm
What to Expect
●These babies can get sick more often than full-term babies, so handwashing is very important for safety
●These babies become tired much faster, it is normal for them to take more naps
●Some smaller babies may need special equipment for care
●The baby is small at birth and it will take some time to catch up to their peers
●Long term survival and thriving is possible
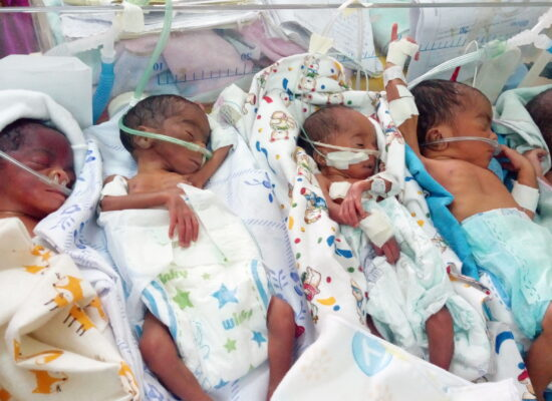
Taking Your Preemie Home

●Breastfeeding is best when possible
●If feeding with formula that needs mixing, boil the water and let cool so that harmful germs are killed, making it safe for the baby
●Skin to skin care is where a wrap is used to keep baby on mom’s chest and can help keep the baby warm and stable
●The safest sleeping position for baby is on their back with no objects near them
Warning Signs to look for
●For all babies
○The baby’s lips turn blue
○Trouble breathing
○Trouble waking the baby
○Fever
○Not eating
○No weight gain
Warning Signs If Baby has a Feeding Tube
Some preemies need to go home with a feeding tube.
These are not needed forever
Baby needs medical help if
- If the tube comes out
- Baby turns blue or changes color
- Coughs or chokes during feeding
Skin to Skin
- Baby should be cleaned off after birth, then placed on the mother’s bare chest
- As much as possible after birth carry or hold your baby in front of you (not on your back) and between your breasts to:
- Promote warmth
- Create a bond between the mother and baby
- Can help stabilize the baby’s and mother’s
- Heart rate
- Breathing
- Temperature
- Helps lower mothers stress and hormones

Preventing Infection
- Newborns are at an increased risk of developing infections because of their immature immune systems
- Ways to prevent infection:
- Wash hands before touching a preemie
- Ask others to wash their hands before touching a preemie
- If others are sick, ask them to to wait before visiting
- Keep babies environment as clean as possible

Breastfeeding Mothers
- Preemies need food to survive
- Breast milk is important for preemies
- More nutrients for baby
- Preemies have trouble feeding because they have a poor sucking reflex and tire more easily
- May need more and shorter feeding sessions
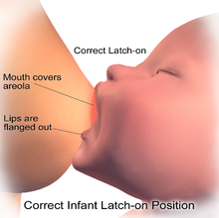
- Ways to know the baby is feeding correctly
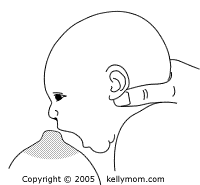
- Latch on
- Audible Swallowing
- Type of nipple
- Comfort
- Holding = the position used by the mother
Swaddling